Cybersecurity secures computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from assaults. It’s sometimes called information technology or electronic security and has become the top 10 problem for every organization and industry. So how can organizations protect data in a highly connected global digital landscape? Organizations are placing critical data at risk with more services and devices connecting to the internet. As the potential bounty climbs, so does the chance of a hack or incursion, which can be devastating. Let’s look at these ten cybersecurity checklists to analyze risk, detect threats, decrease susceptibility, and boost preparation.
1. Network security
Company equipment and networks must be secure to prevent cyberattacks. Antivirus software alone may not prevent assaults—update software with the latest viruses and malware. If your router/firewall is old, consider updating to modern hardware and real-time monitoring. Update your firewall and endpoint protection solution. Don’t make it easier for cybercriminals to attack. Automating software patches is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity.
- *Protect the network perimeter and filter out dangerous content
- *Check security measures.

3. User Education And Awareness – Learn About Phishing Scams
Security education is vital. Employees should receive up-to-date cybersecurity training regularly and should corporate assets from assaults on the newest cybersecurity trends. Know cyber hazards. In phishing, the attacker pretends as the sender to mislead the receiver into disclosing credentials, clicking a malicious link with malware, trojan, or zero-day vulnerability exploit. 90% of ransomware assaults are phishing-related. Therefore, one should know which connections are safe. In addition, employees should be taught cyberattack prevention strategies. Finally, create a risk-aware workplace culture by including cybersecurity training in onboarding.

3. Malware prevention
IT policies must clarify how IT assets can be utilized and what constitutes inappropriate use. For example, develop a company-wide anti-malware policy. Antivirus (AV) software is the most common defense against malware. Secure WiFi with VPN. Add low-cost VPN technology to encrypt staff WiFi internet access to your organization. A firewall blocks hackers, malware, and other dangerous Internet activity and controls what traffic enters your device. Use reliable antivirus software and only one on your device. Windows and Mac OS X have firewalls called Windows Firewall and Mac Firewall. Your router’s firewall should prevent network threats.
4. Timely OS and Application Updates:
Patching outdated software, including operating systems and applications, is one of the most crucial cyber security recommendations for reducing the impact of ransomware. This assists in closing critical security holes that hackers use to gain access to your devices. Don’t make it simpler for hackers to access your system and launch an attack. Software patch automation is a crucial component of cybersecurity. Applications and operating systems must be current to ensure that the most recent security updates are applied.
- Activate your device’s automatic system updates.
- A desktop web browser should utilize automated security upgrades.
- Update the plugins in your web browsers, such as Flash and Java.
5. Use Strong Passwords And A Password Manager
Use strong passwords and a password manager. Strong passwords are crucial to internet security. Passwords protect your data from hackers. NIST’s 2017 revised password policy framework suggests. Dropping uppercase characters, symbols, and numerals, choose a user-friendly password with eight to 64 characters. The password should contain one lowercase letter, one capital letter, one number, and four symbols, but not &%#@.
Never put a password clue out in the open for hackers to notice.
Remember your password. Once a year, renew it.
6. Remotely Backup Data
Backups are an often-overlooked part of online security. Top IT managers adopt the 3-2-1 backup rule. Keep three copies of your data on local and external hard drives and one off-site (cloud storage). You must delete your machine and recover from a backup if you get ransomware or malware.
7. Avoid Public WIFI
Use a VPN on public WIFI (VPN). Using VPN software encrypts device-to-server traffic. Cybercriminals will have a more challenging time accessing your device’s info. If security is vital, use your cell network. Internal and external vulnerability checks: Conduct internal and external vulnerability tests to understand system flaws and vulnerabilities. For example, internal scans check for hazardous applications, and exterior tests assess network segmentation and isolation. Penetration testing simulates assaults to find system vulnerabilities and address undiscovered faults.

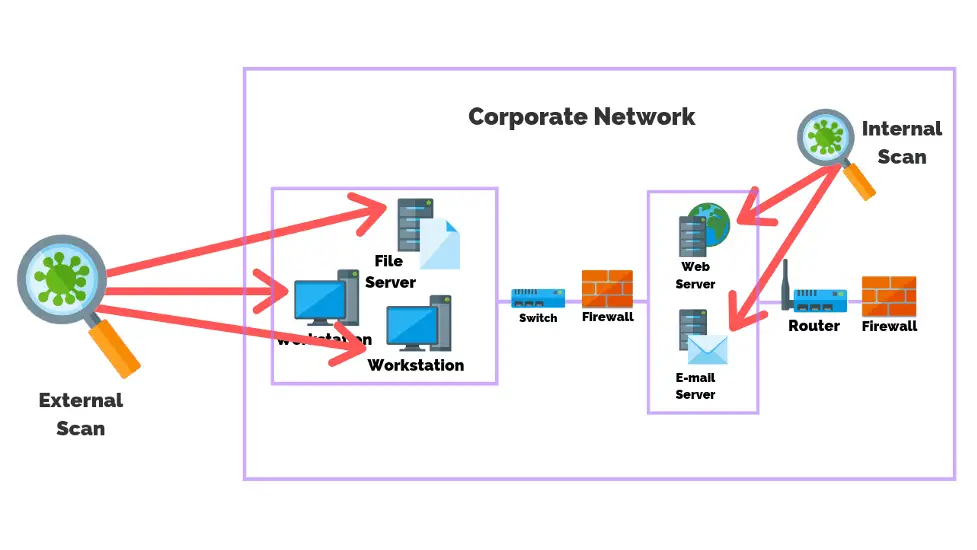
8. Internal And External Vulnerability Checks
Conduct internal and external vulnerability tests to understand system flaws and vulnerabilities. For example, internal scans check for hazardous applications, and exterior tests assess network segmentation and isolation. Penetration testing simulates assaults to find system vulnerabilities and address undiscovered faults.
9. Encrypt Laptops
Encrypt all laptop disc drives. This is crucial if you hold financial and credit card data. For example, Apple computers contain built-in encryption. You may buy Windows and Android encryption software.

10. Plan Security
Develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy to avoid cyber threats, detect vulnerabilities, and reduce data breach damage. Consult industry professionals to make business-risk decisions about your company’s cybersecurity.