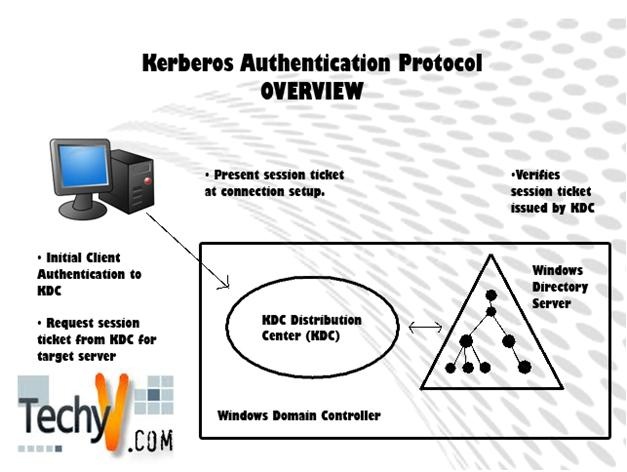
What is called Cyber Security?
Information technology security or computer security or cyber security is the preservation of the vulnerable programs, information, data, hardware, software or the machine infrastructures entirely from a wide range of theft, damage, unauthorized access or cyber terrorism. The risks include code injection, illegal activity by the user, operator misuse.
What are the components of cyber security?

IT security covers the vital areas such as:
1. Network Security- It is primarily concerned about the safety of the network by monitoring misuse, unauthorized access of the resources.

2. Application Security- Protection of the application’s lifecycle against the threats that gets embedded during the application’s development, upgrade, maintenance, or deployment.
3. Information Security- Securing sensitive data and information from the damage, revelation, disruption, alteration.

4. Disaster recovery- The recovery of the lost information when in an emergency or in natural or human-induced disaster.
5. End-user education- People working on the security system need to learn and study about the procedures and the protocols.
What are the types of security risks and threats?
i. Malware- It includes Cyber threats such as:
• Worms- Worms are those threats which only spreads from one machine to another or even through the internet, without harming and changing the settings of the computer. The drawback is that it fills the hard disk by copying the bandwidth.
• Viruses- It affects the programs by replicating and hence the user is unable to handle the computer properly.
• Trojans- It helps cyber-criminals keep a track on you, steal, block, modify, copy the data and information. It will even lead to damage of the entire security system.
• Spyware- It acts as a spy on the user’s computer and its daily activities id recorded, and it gets connected to the host of the malware.
ii. Backdoor-
Installation of the Backdoor before the infection of the Trojan or the virus helps the transfer of the threats. It can even lead to the rebooting of the computer as the author wishes.
iii. Distributed Denial of Service(DDoS) –
The attackers steal the data, send the huge amount of traffic or data by making lots of connection requests that overload the system and hence disabling the security feature.
iv. Phishing-
A fake website resembling the real one which requires the user to enter their username, password into a forgery login form or the users are asked to click on the link. By this way, the attackers enter the personal information.
v. Rootkit-
It prevents the detected malicious program so that the injected threats can run smoothly.
vi. SQL Injection Attack-
It attacks the server that contains the data for websites and services and which uses SQL to manage the information.
vii. Botnet-
Whenever someone visits the page, the user’s system downloads a program. It infects through drive-by download or may be Trojan infection.
viii. Cookies-
It has the tendency to store information into the user’s computer and track the activities within site.
ix. Wabbits-
The self- replicating threats that do not harm the machine but divides via the LAN network like the worm.