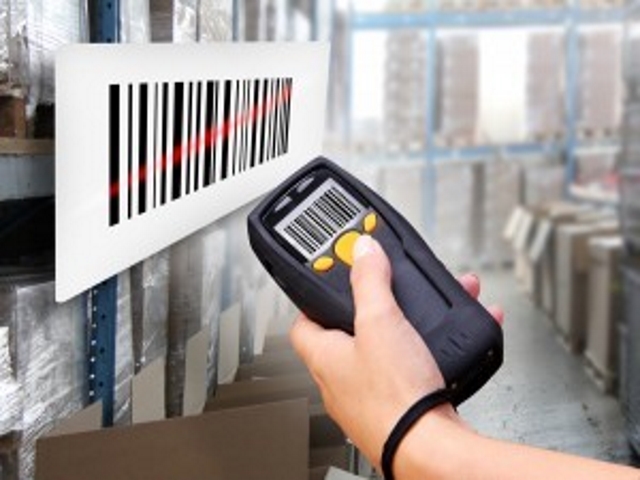
Today, many business centers, hospital settings, and other information technologies company use the growing technology of barcode scanning. The barcode scanning is being widespread in many areas and nations that people use it to this advantage and even few misuses it. The primary principle behind barcode scanning is symbology. Symbology is the one which provides the necessary form of a barcode.
A barcode is a machine-friendly and an optically linear representation of a particular product’s data. The basic structure or idea of a barcode is black stripes denoted by a few numbers below the lines and will be scan-able under the scanner. This technology with a large arena for scope and usage has its respective pros and cons.
Few BARCODE WITH THEIR USES:
- Farmacode or Code 32- Italian pharma code.
- CODE 39- international standards (ISO).
- CODE 49- discrete used in many areas.
- CODE 93- continuous used in many areas.
- Codabar- blood-banks and libraries.
- EAN 2 and EAN 5- magazines and books.
- Intelligent mail barcode- United States postal service code.
- Facing Identification Mark- business reply code for emails.
- MSI- inventory purposed and warehouse uses.
ADVANTAGES OF BARCODE SCANNING:
Workers and professionals can reliably search and find products and packages without any manual work tension. Human errors are reducible since machines like printers and scanners are useful for scanning purposes. Reading the encoded message or information is usually done quickly. For example, in a supermarket, clerks can bill the respective items purchased by a consumer very quickly by scanning the product’s barcode using a scanner and can give the total products and its value simply. Few industries like the transportation sectors use barcodes to differentiate one product from another and to verify new ones from old ones. Labeling the packs or things with barcode is today budget-friendly and is efficiently processed just through your mobile phones and computers.
APPLICATIONS OF BARCODES:
- Barcodes are being used in libraries to check the availability of a book, whether a book is to be issuable or not, also to keep general tracking if the records maintained.
- These barcodes are applicable also in laboratories for identifying the ingredients used in a chemical, to differentiate one substance from another, and also to study some chemical’s composition vaguely through scanning.
- Barcodes are useful in different industrial sectors of work.
- In hospitals, barcodes play a vital role in billing medicine quickly and also to find drug’s place in the pharmacy.
- These days, even mobiles use barcode scanners to verify an item’s durability and to check if the mentioned detail is there in the product in real.

IMPORTANT FEATURES OF BARCODES:
- Identification number uniquely represented.
- The extraordinary accuracy of the information.
- Work measurement made easier.
- Data collected up-to-date.
- Barcodes avoid human errors.
- Cost-effective.
CONS OF BARCODES:
Even though there are advantages of barcode scanning, the disadvantages are also given extra consideration. Since the barcode scanning is a manual method, there are chances of system failure. When a device for scanning gets damaged, there exists unnecessary confusions and improper work pending. Trouble arises when a barcode is not clear, scratched, or if crumpling seen due to some defect. The data or information in a barcode has to store already or given inputs in the scanner.
Henceforth, barcode scanning is plus on one hand and minus on the other and depends upon the type and duration of using it.