What Is AI-enabled Autonomy?
AI-enabled Autonomy is the ability of machines or computer software to perform individual or direct human intervention, but inside constraints, to achieve a goal or solve a problem.
How Could AI Be Pre-owned In Cyber And Information Warfare?
AI is predicted to convert both how actors defend against and begin cyber-attacks. For instance, systems with AI and machine learning abilities could simultaneously search for threats in enemy systems to utilize while also observing weakness in their systems. When coming under attack, they could immediately and impulsively launch counter-attacks.
These forms of changes could increase the extent of cyber-attacks while also changing their character and severity, particularly in terms of unfavourable consequences on citizens and civilian structures.
Moral And Legal Implications
Autonomous Weapons – Autonomous warfare inhibited by artificial intelligence can choose and manage targets without human intervention. The issue of liability in involuntary damage is a pressing error.
Bias and Discrimination – AI algorithms can accept bias from their training data, leading to potential prejudice in target alternative or vulnerability evaluation. It has critical moral implications and may conflict with international law.
Protection and threats – AI systems can be attackers or manipulated, leading to unexpected results or abuse. Ensuring the protection and integrity of AI systems in war is a supreme challenge.
Transparency – A lack of transparency in AI decision-making procedures can make it problems to insight because a particular action was taken, creating a problem to manufacture intent in supposed war crimes cases.
International Regulations – There is a developing requirement for international deals and regulations to govern the use of AI in warfare. The growth of AI particularly arms control accord is an urgent essential.
1. Precision Strikes
One of the most outstanding applications of AI in warfare is its capability to benefit precision strikes. Autonomous warfare powered by AI can define and integrate opponent positions with unparalleled accuracy. These systems can adapt to dynamic ground situations, making them highly adaptable and efficient devices in the advanced arsenal.

2. Surveillance And Reconnaissance
In surveillance and reconnaissance, AI-enabled drones have arisen as costly assets. These drones offer time intelligence by catching high-resolution imagery and observing enemy actions. AI algorithms evaluate this data to recognize potential vulnerabilities and threats, providing military commanders a crucial advantage.

3. Offensive Abilities
AI-driven offensive ability in cyber warfare is a significant change. Malware and hacking devices, powered by AI, can penetrate enemy networks, are disturb crucial structures, and agreement communication systems. These AI-based assaults are converted, adaptive, and frequently tricky to observe, making them brutal weapons in the hands of nation-states and malicious actors.
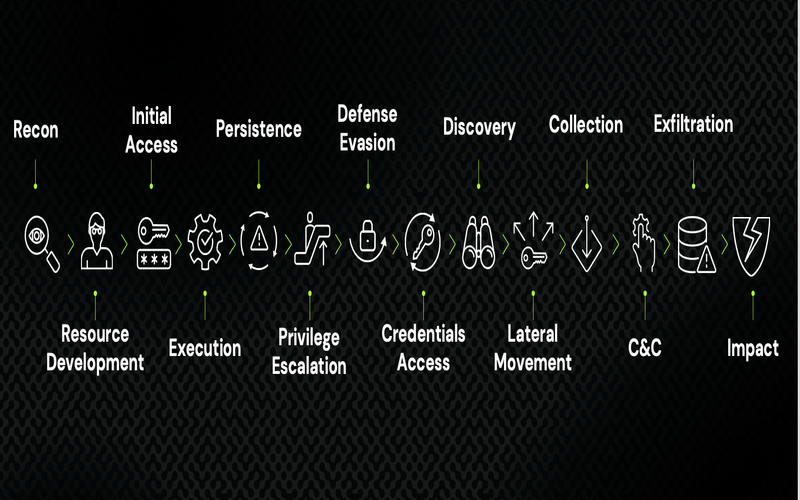
4. Defence Mechanisms
AI is pre-owned for violation in cyber warfare, it is equally critical for defence. AI-powered cybersecurity systems consistently observe networks for potential vulnerabilities, recognizing anomalies and threats in actual time. These cautions improve the security of military and government networks, securing sensitive details and avoiding cyberattacks.

5. Predictive Analysis
Another essential role of AI in modern warfare is predictive evaluation. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data, involving historical battle records, weather patterns, and geopolitical details, to forecast enemy movement and objectives. This ability enables military commanders to make more informed decisions concerning troop employment, resource allocation, and method planning.
6. Logistics And Supply Chain Management
Effective logistics and supply chain management are the driving power behind any military employee. AI streamlines these techniques by observing routes, managing registers, and forecasting keep-up requirements. It assures that vital resources, such as ammunition, medical supplies, and fuel, approach the cutting edges instantly. By decreasing logistical bottlenecks and enhancing resource allocation, AI improves the overall efficiency of military duties.
7. Ethical And Legal Concerns
The engagement of AI in warfare boosts ethical and legal questions. Errors such as accountability for autonomous systems, agreement to international law, and the potential for intended outcomes pose challenges that need careful consideration.
8. Human-Machine Collaboration
AI works alongside human employees to boost overall military quality. Human-machine collaboration enhances effectively, enabling soldiers to focus on complicated decision-making while AI controls routine tasks, leading to a more efficient and adaptive force.

9. Autonomous Weapons Systems
Autonomous artillery, powered by AI, can separately recognize and merge targets without direct human interposition. These systems scale from drones to ground-based vehicles and are patterned to improve operational effectiveness and response times.
10. International Competition
AI-enabled warfare has developed into a primary point in international competition connecting nations. The race to observe and retain modern AI innovation in the military broad is autonomous in the developing importance of AI as an incentive for diplomatic authority and the army dominance.

Transforming The Latest Algorithm Of Battlefield
AI will bring a shift in the features of war, but not in the behaviour of the battle itself. In the UK, the Taranis drone, an uncrewed constant aerial transport, is predicted to be operational by 2030 and capable of returning the human-piloted Tornado GR4 fighter aircraft that are part of the Royal Air Force’s future Offensive Air System. Adjusting AI in words of using artillery has potential implications for the war algorithm. For the military, object recognition is a logical beginning point for AI, as it needs data of many distinct kinds such as selecting thousands of such as images, and voice data, and offering observation on the targets and details gathered from satellites. This is why drones are searching their way in the military battle rooms. In the year of fast development of the third stage of artificial intelligence systems, we will see more of the brutal soldiers in the field of mission.