A router serves as the critical central hub directing traffic across a home or office network, and enabling connectivity both between local devices and to the broader internet. Suboptimal router configuration often underlies frustratingly intermittent connectivity, lagging speeds, and full network meltdowns necessitating tedious reboots. To facilitate seamless network connectivity enabling rapid data transfers and uninterrupted streamed content across devices, I outline actionable router configuration best practices.
During scheduled maintenance windows — when the risk of brief downtime matters less — I recommend implementing as many tweaks as feasible across firmware, settings, placement, and accessories to realize a transformation in network resilience and performance. As part of regular reporting, network performance metrics and connection latency across test cycles warrant close monitoring to identify the most consequential configuration changes.
Specific settings lead to dramatic upticks in network throughput, and over extended periods certain adaptations prove instrumental in slashing downtime frequency. Streamlined router dashboards provide visibility into settings optimizations over time as warranted based on evolving network demands.
1. Choose A Business-Grade Access Point
For home networks seeking to support 20 or more concurrently connected devices, consumer-grade routers inevitably falter under the load. Stepping up to advanced hardware such as high-powered Tri-band MU-MIMO routers or mesh systems better shoulders intensive bandwidth burdens imposed by additional laptops, phones, TVs, and other smart home gear connecting, streaming, and transferring data simultaneously. Business-class hardware offers increased wireless range and more robust internal components to maintain swift speeds even with many active Wi-Fi clients, although tradeoffs emerge given substantially higher costs reaching hundreds of dollars per access point.

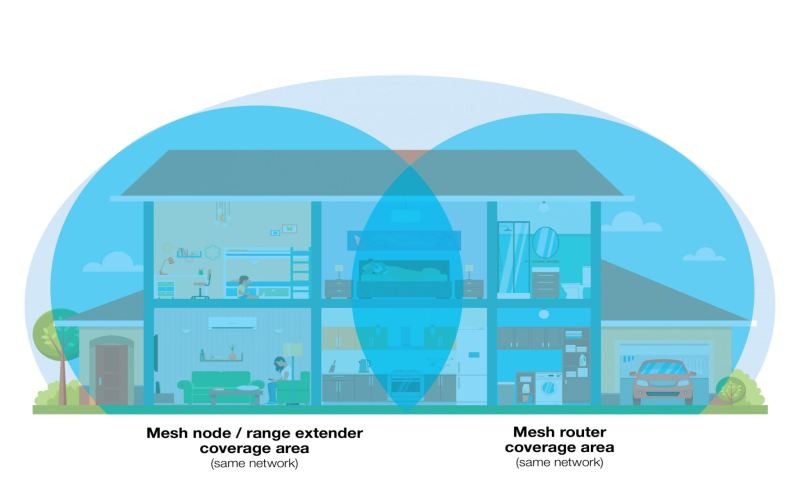
2. Consider Using A Mesh Router System
Within larger homes spanning over 2,000 square feet or across multiple floors, single consumer-grade routers battle to blanket full spaces with strong and stable Wi-Fi. The radio signals attenuate too significantly for fast speeds in the farthest corners. Mesh router kits comprising multiple compact access points strategically dispersed throughout spaces help achieve full-home coverage. While streaming a 4K video in a distant bedroom, seamless roaming capabilities also enable smoothly transitioning the active connection to the new nearest mesh node without service interruption as someone crosse the house.
3. Use A Wi-Fi 6 Router
The recently finalized 802.11ax Wi-Fi protocol, marketed as Wi-Fi 6, unlocks substantial performance and efficiency upgrades for networks straining under a load of today’s device multitudes relative to preceding 802.11ac Wi-Fi 5 routers. Alongside tight 4×4 MU-MIMO support for simultaneous connections, OFDMA bandwidth partitioning introduces more responsive concurrency. Wi-Fi 6 routers better handle many active clients like the explosion of smartphones, tablets, laptops, TVs, and smart home devices found in modern households. Target Wakeup Time events also trim power inefficiency, while still enabling a rapid return to active transmitting state when data needs sending.

4. Optimize Your Router Placement
Router visibility represents just the tip of the iceberg when configuring for optimized performance. The location where one situates the actual router hardware bears equal importance, although often proves secondary consideration out of convenience. Mounting high in central areas absent thick walls and other signal barriers takes advantage of unobstructed straight-line transmissions to deliver the farthest reaching, fastest coverage. Nearby appliances also sometimes interfere with crowded channels. Testing alternative placements while monitoring signal strength identifies layout adjustments delivering full-bar connectivity to previously struggling spots.

5. Update Your Router Firmware
While not tweaking any functional settings per se, downloading and installing the latest router firmware imparts hardware fixes, security patches, and general performance enhancements. Yet many neglects this crucial router maintenance despite significant upgrade consequences. Outdated firmware undoubtedly leaves one more vulnerable to hackers while also limiting speeds and possibly contributing to crashes. Network equipment manufacturers continuously issue firmware updates responsive to discovered product shortcomings or evolving compatibility demands.

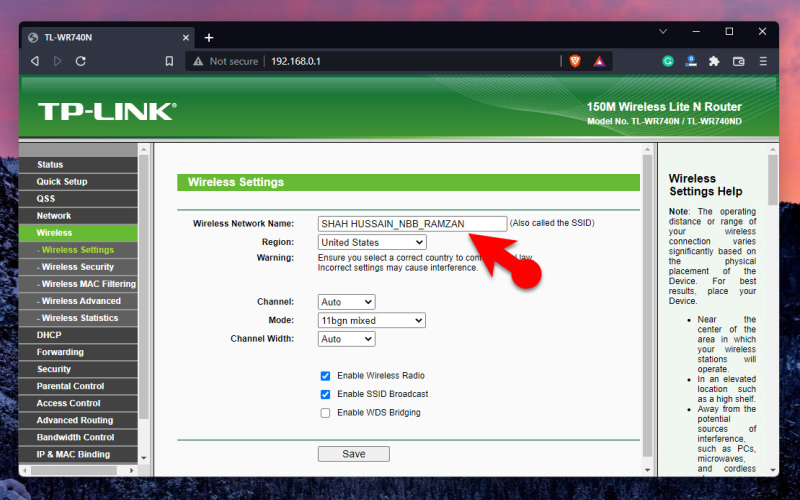
6. Check Your Router Settings
Venturing into the router’s administrative interface presents the most direct means of fine-tuning performance beyond physical placement. Default configurations universally fail to unlock full-speed potential. Toggling settings alter how aggressively devices compete for bandwidth, which channels get utilized, how many devices connect concurrently, and how intelligently limited capacity gets split. something as basic as broadcasting separate network names for the 2.4GHz versus 5GHz bands decreases congestion by automatically distributing devices. Authentication modes, channel widths, transmit power and DHCP address pools warrant tailoring for specific network needs. Just take care not to activate features one’s internet subscription cannot serve like enabling Multi-Gig.
7. Use A VPN Service
Accessing region-restricted content represents one common personal motivation for connecting through a VPN, although broader security and privacy appeals also abound. Routing traffic through an intervening server using a protocol like OpenVPN before reaching the open internet allows for obscuring one’s public IP address and physical location. This protects against location tracking, blocks ads, and bypasses filters. VPNs also encrypt data over the intermediate path spanning one’s device and the VPN server to reduce opportunities for snooping attempts across open Wi-Fi.

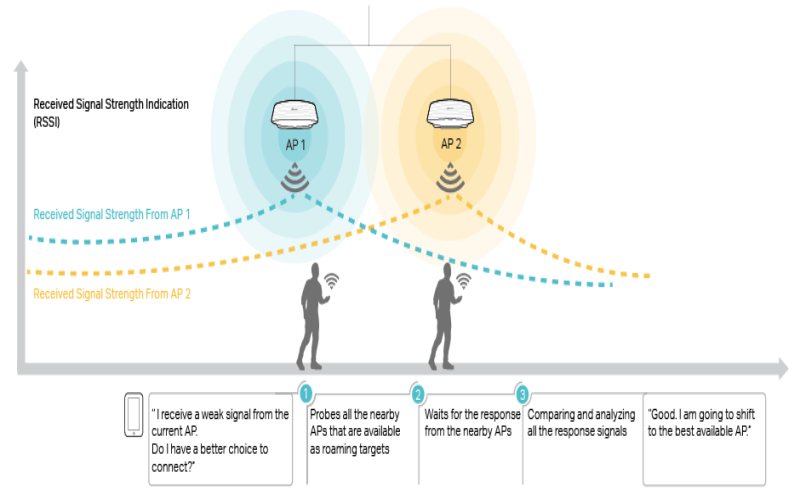
8. Enable Seamless Roaming
Inside Wi-Fi settings on client devices, enable auto-connect functionality to automatically jump networks as one physically moves across extended spaces. As someone crosses between access point coverage zones, the device can experience temporary disconnects from the former router before identifying and connecting to the new alternative router. Quick connect prevents app buffering or session timeouts during the transition. On iPhone devices, enable the Auto-Join feature under Wi-Fi settings. For optimal compatibility, use a Wi-Fi 6 mesh router system with band steering further facilitating smooth client roaming between nodes.
9. Use A Guest Network Access Feature
While friends visiting likely appreciate easily connecting phones and laptops to Wi-Fi for internet access, offering credentials to one’s main network proves problematic given the potential to access shared files and other connected devices like network hard drives or printers. Compromise by configuring a separate guest network with its own SSID and password. Guest networks logically segment visitor devices in keeping sensitive primary network resources restricted without the need to continually provide and revoke designated visitor passwords.
10. Monitor Your Network Performance
Without routinely monitoring connection metrics before and after changes, one cannot quantify the impact of attempted router optimizations. It proves crucial to collect baseline measurements during typical usage, and then retest after firmware updates, location changes, and settings modifications to gauge measurable speed and reliability improvements. Monitoring also alerts to unexpected new issues like interference from external signals suddenly congesting previously free channels. Use router utilities, online speed tests, or Wi-Fi analytics apps to continuously inspect metrics like latency, jitter, and transfer rates.