Microsoft Active Directory Universal, Global and Local Security and Distribution Groups
When we conceive a new assembly in Microsoft Active Directory, we should choose an assembly type. Two of the assembly kinds are described as follows:
1. Security Groups in Active Directory:
Such assemblies permit us to organize client and PC to get access to distributed resources. We can also command who obtains assembly principle settings. It makes management easy by allowing us to establish permissions one time on many PCs, then to change the members of assembly as required. The alteration in assembly members mechanically affects all over. We can furthermore employ these assemblies as internet note circulation lists.
2. Distribution Groups in Active Directory
Such assemblies are proposed to be utilized only as internet note circulation lists. These registers can be employed with internet note submissions, for example Microsoft Outlook or Microsoft Exchange. We can add and eliminate associates from the register on the account that whether they ‘will’ or ‘will not’ obtain internet note dispatched to the circulation group. Besides, we are unable to employ circulation assemblies to accredit authorizations on anything. Here, we’re also unable to employ them to filter assembly principle settings.
In short and simple words, the security groups can be utilized for the purpose of permission settings and emailing. On the other hand, when it comes to the distribution groups, they can only be used for the purpose of emailing. Both of these two groups are normally created in Active Directory and both can be used for users within the domain.
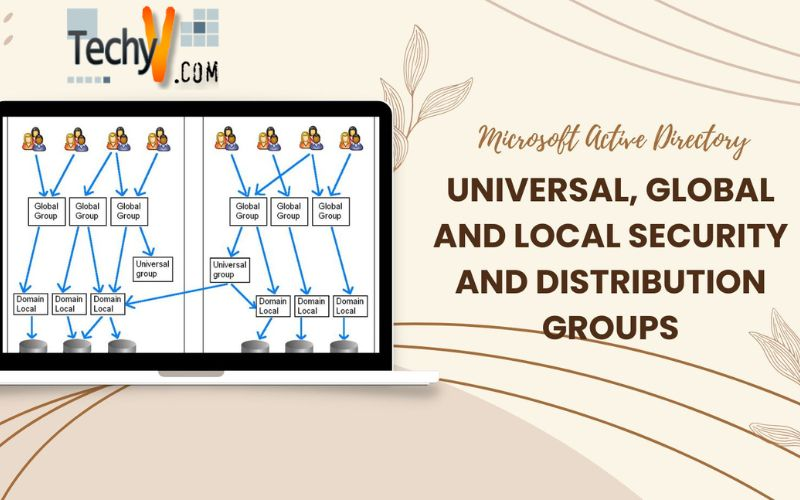
Defining Universal, Global and Local Security and Distribution Groups in Active Directory
Well, when it comes to a domain localized group, it is a protection or circulation assembly that can comprise universal assemblies, international assemblies and other domain localized assemblies from its private domain, and also anecdotes of any of the domain that is in the forest. We’re able to assign domain localized security assemblies privileges and authorizations on assets that are solely in the same domain.
An international or global group is an assembly that you can utilize in constituent servers, in its own private domain, in domain workstations and in believing domains. You can give an international assembly privileges and authorizations in all those positions, as it can become a constituent of localized groups. Furthermore, an international assembly can comprise client anecdotes, which are solely from its private domain.
A universal assembly is generally a security or circulation assembly, which comprises of users, assemblies, and PCs from any domain in its plantation as ‘members.’ You can give privileges and authorizations to the universal security assemblies on assets in any domain in the forest. Such kinds of assemblies are usually not supported.
If you’re willing to employ a single domain for your entire servers with no WAN lives, you’re suggested to employ domain localized groups. You cannot employ the catalog of a global domain for a localized domain. Also, remember that the ‘Electronic Data Interchange’ (EDI) adaptor is not conceived to be configured for localized group domain. On the contrary, you can configure it for global groups of domains.
Apart from all this, if you wish to keep a multiple.domain topology with the next situation factual, you’re suggested to employ global groups’ domain:
1. You can find an SQL Server.based server in the facts and numbers hub.
2. You have a boundary mesh, which is also known as the screened subnet or DMZ (demilitarized zone).
Being one of the most established world wide web servers of the Microsoft, the ‘Internet Information Services’ (IIS), has been considered a feeble issue on a server, especially from the protection point of view. This very environment of the web servers is usually open to the new media, until and unless someone utilizes them solely to access intranet. All this collectively gives favor to the intruders and attackers because it becomes their natural goal this way.
Enhancements and Features of Windows 2008 Domains in Active Directory
Following are some of the major enhancements and features that have been added to the Windows 2008 Domain:
1. Read Only Domain Controllers (RODC)
This feature can be commonly utilized at such locations where the tangible protection of the domain controller is below to par. This feature allows you to identify locally stored passwords in order to lessen threats of losing passwords especially if the domain controller has been accessed by intruders or stolen. It also has a Read.Only DNS function.
2. Role Based
The server roles have also been defined to bring ease to the system installation process, lessen repairs, possible protection vulnerabilities, and without activating the server, The MS Windows 2008 Domain Server auto.installs any roles. Some of these roles are:
- Active Directory Certificate Services – ADCS
- Active Directory Federation Services – ADFS
- Active Directory Right Management Services – ADRMS
- Application Server – AS
- DHCP, DNS and Fax Servers
- Windows Deployment Services – WDS
- Web Services
Some of the other enhancements provided by the Windows Active Directory Server 2008 include
1. Server Core
2. Forest Functional Level Features, which further includes:
- Fine.grained Password Policy Changes
- DFS Replication for SYSVOL and
- Advanced Encryption Services
3. DCPromo Enhancements
4. Restartable Active Directory Domain Services
5. Database Mounting Tool
6. Audit Policy Changes
7. DNS Enhancements, which further includes
- Background Zone Loading
- Enhanced IPv6 Support and
- Global Names Zone
Enhancements and Features of Windows 2003 Domains in Active Directory
Like Windows Server 2008 Domain, Windows 2003 Domains were improved with the addition of new features including high.level security. Following are some of the updated features and enhancements which were added to the Windows 2003 Domains in AD:
1. IIS Security Enhancements
a. No IIS Installed by Default
b. Lockdown Mode
c. New Authentication Method
d. URL Authorization
2. Extra Active Directory Authentication Enhancements
a. Active Directory Application Mode
b. Credential Manager
c. inetOrgPerson Compatibility
3. Group Policy Improvements, which came up with the following sub nodes:
a. Domains
b. Sites
c. Group Policy Modeling – it is the latest name used against the ‘Resultant Group Policies’ in ‘Planning Mode’
d. Group Policy Results