Today, technology is evolving faster, and IT professionals should realize that their title role may not stay the same in a contactless world tomorrow. Constantly learning and re-learning is a necessity. To secure a safe job, we need to watch the latest technologies. Technologies like AI, ML, Big Data, IoT, Angular, Data Science, etc. are in great demand. Some of them are mentioned below:
1. Artificial Intelligence
This term was first used in 1950 by Alan Turing. It is the mimic of human intelligence by machines, especially computer systems. Intelligence is not just one characteristic of a human being but the ability to adapt to diversity like learning, reasoning, problem-solving, using language, and perception, which AI has also focused upon. AI involves training and analyzing data for correlation and pattern and using this data to predict future states. Technologies under AI include Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Pattern Recognition, Image recognition, Biometrics, Cognitive computing, etc.
2. Quantum Computing
It is challenging to solve significant complex problems using classical computers, which use bits to store information represented by either 0 or 1. But quantum computing is a technology that allows us to solve these problems in a short time frame using qubit, 0, and 1 simultaneously. Quantum computers work on quantum principles that include entanglement, superposition, and decoherence. It can contribute significantly to fields like Big Data, Finance, Genetic Engineering, AI, Machine Learning, etc. Some prominent companies like Google, IBM, Microsoft, etc., are working on this technology.
3. Metaverse
Metaverse is not any specific type of technology but rather how we interact with a particular type of technology, including Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and blockchain that allows people to interact with each other. This term was first used in 1992 by sci-fi writer Neal Stephenson in his novel “Snow Crash.” He described the “metaverse” as a 3D virtual space people could occupy. Metaverse can be used in e-commerce, interactive learning environments, mass audience interaction, real estate, healthcare, and fashion.

4. Data Science
Data Science is a domain that deals with three different aspects of data, i.e., its design, collection, and analysis. After this, meaningful data is extracted for business, it combines various principles from mathematics, statistics, AI, and computer engineering to analyze large amounts of data. Data science uses tools like R Studio, Python programming, and machine learning algorithms to build predictive models. The Data Science lifecycle involves five stages – capture, maintain, analyze, process, and communicate. It has various applications, including healthcare, logistics, speech recognition, fraud detection, and targeted advertising.
5. 3D Printing
It is a process of making three-dimensional objects from digital files. It is also known as additive manufacturing, i.e., adding material in various ways. It facilitates us to produce complex shapes using less material than traditional manufacturing. 3D printing needs high-quality materials to build high-quality devices. It includes ceramic, metals, composites, innovative materials, unique materials like lunar dust, and polymers. 3D printing can be used in various fields like aerospace, food, healthcare, medical, construction, fashion, and electronics.

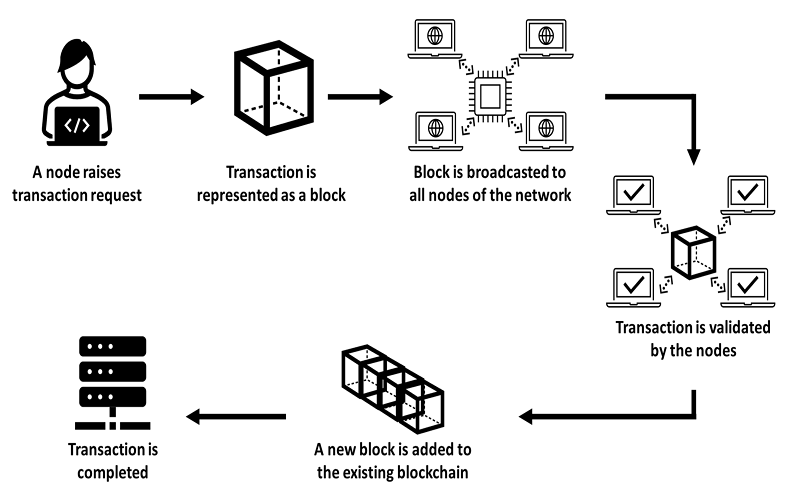
6. Blockchain Technology
It is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that stores the data of the public in several databases. Here, data is stored in blocks that are linked together in a chain. It differs from a typical database as it stores data using cryptography. It is decentralized so that no single user has control over it. In Blockchain technology, information runs through an encryption algorithm, which creates a hexadecimal number called the hash. Blockchain gives transparency and traceability and allows a customer to verify the origin sustainability of a product. Blockchain can be used in finance, healthcare, digital currency, supply chain, and voting.
7. Cyber Security
Cyber Security refers to protecting sensitive information from cyber attacks like phishing, ransomware attacks, data breaches, etc. It includes technologies, processes, and methods to protect computer systems, data, and networks from attacks. It is divided into various subdomains – application security, cloud security, mobile security, identity management and data security, and network security.

8. Cloud Computing
It refers to the on-demand delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet to offer faster services. There are several benefits of cloud computing – it lowers IT cost, gives easy access to a broad range of technologies such as database, IoT, ML, and much more, provides elasticity, and deploy globally in minutes. Three main types of cloud computing include Infrastructure as a service, software as a service, and platform as a service. Some big players include Google Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud.
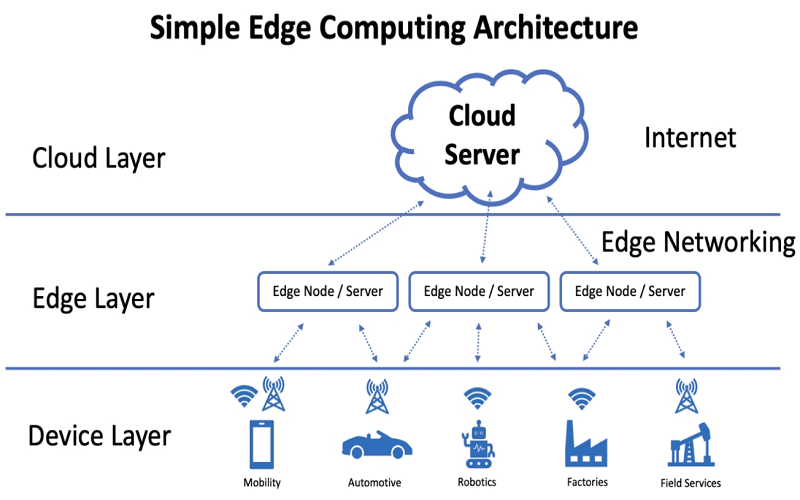
9. Edge Computing
To enable faster response time and lower latency in cloud computing, edge computing came into the picture. The idea of edge computing is to analyze data locally in real-time, closer to where it is stored, rather than sending it away to the centralized data center. It is a quick and data-efficient technology. Edge computing has applications including self-driving vehicles, security, medical monitoring, video conferencing, and enhanced customer experiences.
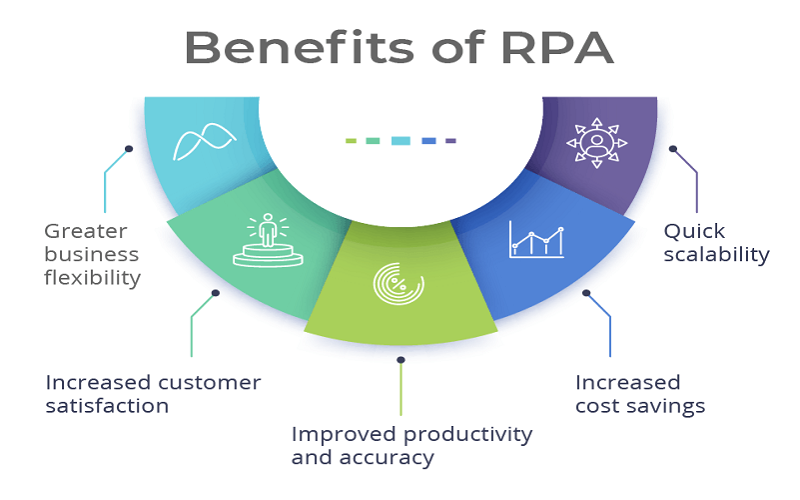
10. Robotic Process Automation
RPA is a software robot that mimics and executes rule-based business processes. It is used to automate various tasks, including data entry, extracting data, moving files, etc. Multiple benefits of RPA include less coding, higher customer satisfaction, cost savings, and better accuracy and compliance. The five primary tools in RPA are UiPath, Blue Prism, Automation Anywhere, Kofax Kapow, and NICE. It can be implemented in industries like Banking and Finance, Insurance, Retail, and healthcare.