What Is Multi-Cloud?
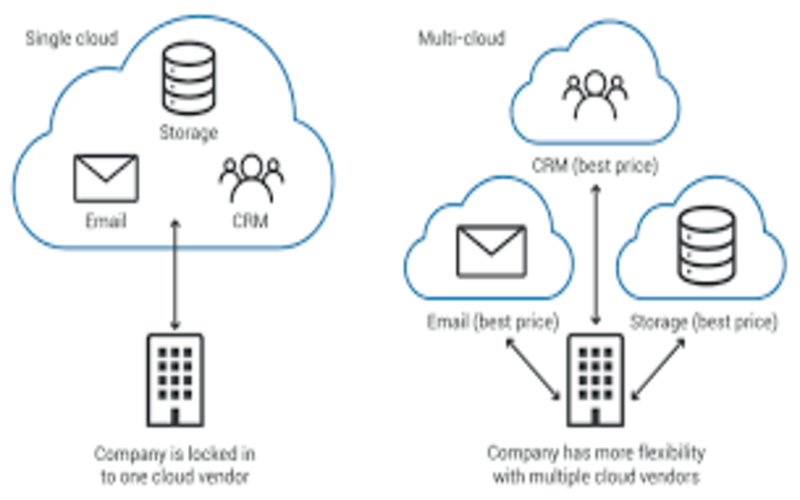
Multi-cloud refers to defined the use of multi-cloud computing services. It generally involves using a mix of public and private clouds from more than one cloud trader for different applications or workloads. Multi-cloud can provide greater flexibility and scalability than relying on a single provider. It can also assist trader lock-in and reduce costs by enabling you to benefit from each provider’s best features and pricing.
What Are Multi-Cloud Architectures?
The multi-cloud architecture is a form of cloud computing decisions that operate services from multi-cloud offers simultaneously. About 92% of companies are already using a multi-cloud decision to admit specialist services and support from various cloud entities. Depending on computer architecture or a single cloud environment to organize all business needed, management uses multi-cloud solutions to match services. A multi-cloud architecture can involve two or more public clouds, more than two “private clouds, or a merging of both—some multi-cloud decisions also authority edge computing cloud innovations.
Why Use A Multi-Cloud Solution?
Today’s management is turning to multi-cloud solutions to take advantage of the advantages that each separate cloud provider has to offer. According to a VMware survey, around 41% of firms that use multi-cloud have witnessed a decrease in cost and more minor hours spent on IT. Consistently speaking, multi-cloud platform solutions can enhance repetition, performance, and security. Businesses can reduce the risk of outages and data loss using various providers. It enables businesses to evaluate their workloads for distinct regions or data types. The solution also gives businesses more choice and reliability, resulting in a competitive advantage. There are 5 points to observe when making a successful multi-cloud architecture:
- Evaluate your whole network and then decide which one of a single cloud service offers is best for your particular needs to reduce the problem of your system and the ineffective use of resources.
- Multiple cloud providers maximize the amount of low-level maintenance and observation. It’s best to mechanical them.
- Concentrate on a similarity of policy, which is impulsively practical to every cloud environment. These strategies cover such topics as storage of data, workloads and traffic flows, virtual servers, regulations, security, and reporting.
- Employ data center management software designed especially for virtual environments. It helps manufacture a system where your server, network storage, operations, security, and application groups collaborate to achieve the same goals.
1. Better Agility And Flexibility
Multi-cloud management can be more agile as they rapidly scale up or down their operation of different services based on their needs. Having admitted to such an option assists enterprises in saving money as they only pay for the resources they use. Multi-cloud can aid companies in building tougher systems as they can retrieve rapidly from any errors with one GSP by using the services of another.

2. High-speed Structures
Many businesses need a high-speed structure to support their duties. By using a multi-cloud structure, businesses can get the best feasible performance as they can use the service of various CSPs with the quicker and most flexible structure. Multi-cloud is significant for organizations that want more control over their cloud services, require more agile duties, or need high-speed structures. By using various CSPs, they can make a customized solution to their specific needs and prevent being locked into one trader.
3. No Trader Lock-ins
When businesses use various CSPs, they are not secure into one trader. Having this reliability means they can switch to another CSP if they are miserable with the service or the costs become huge. This reliability provides businesses more control over their cloud services and assists them in being secure in a long-term contract with one trader.
4. Maximizes Risk Management
Businesses are continuously examined for ways to organize risk better, and one way to do that is to distribute their data and workloads around different cloud services offered. Using various CSPs can assist businesses in keeping their data safe and secure, and it can also help them in preventing outages and other disruptions.
5. Enhanced Reliability And Redundancy
Multi-cloud setups improve reliability by distributing workloads around multi-cloud platforms. If one giver experiences downtime or an outage, the management can modify traffic and workloads to substitute giver, ensuring consistent operation and decreasing the effect of disruptions.
6. Cost Optimization
Multi-cloud environments allow management to evaluate costs by selecting the most cost-efficient services from distinct providers. It enables budget reliability and the ability to arrange better pricing depending on the specific requirements of the business.
7. Improved Performance
Dividing workloads across multiple cloud givers can result in enhanced performance. Management can make decisions to place resources in the data center physically closer to end-consumers, decreasing latency and improving the overall consumer experience.
8. Scalability And Elasticity
Multi-cloud architectures encourage vital scaling and elasticity, enabling management to adapt to changing workloads and requests. This reliability allows automatic scaling of resources up or down depending on actual-time requirements, ensuring optimal performance and resource employment.
9. Calamity Recovery And Business Consistency
Multi-cloud architectures provide robust calamity recovery and business consistency policies. In the incident of a fatal failure or natural calamity moving one cloud giver, management can rapidly switch to selection providers to maintain operations and data honor.
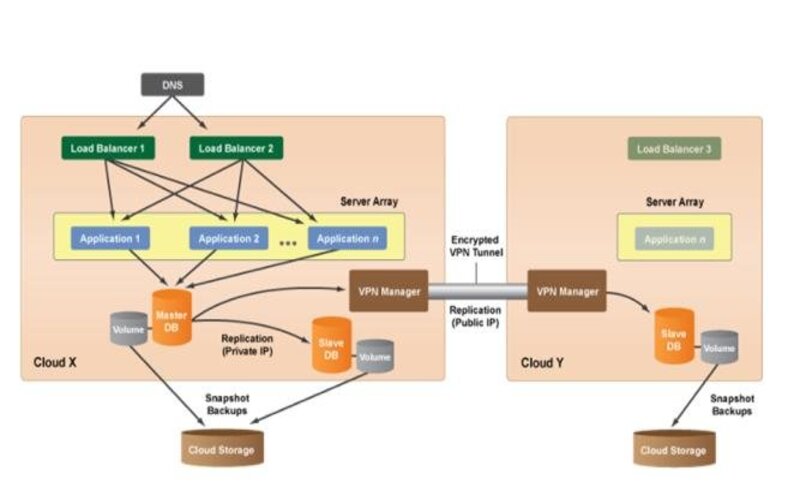
10. Technologies And Best-of-breed Solutions
Enveloping multi-cloud decisions support technologies by enabling management to adapt to new technologies and services provided by distinct providers. Businesses can select the best-of-breed solutions for particular tasks, encouraging a culture of consistent improvement and remaining at the forefront of innovations and advancements.