Agile estimation techniques are crucial in executing agile projects successfully. Agile methodologies have become popular due to their unique approach in delivering the product compared to the traditional methods.
Agile is a project management strategy focusing on short time frames and iterative methodologies in project completion. Companies utilize agile methods to streamline their workflow procedures.
Agile estimation is a process that measures the time and effort needed to complete a project. The primary objective of agile estimation is to achieve improved decision-making, risk management, and better coordination among the team members. Project teams utilize Agile Estimation techniques to calculate a project’s timeline and allocate resources to each project based on the estimation results.
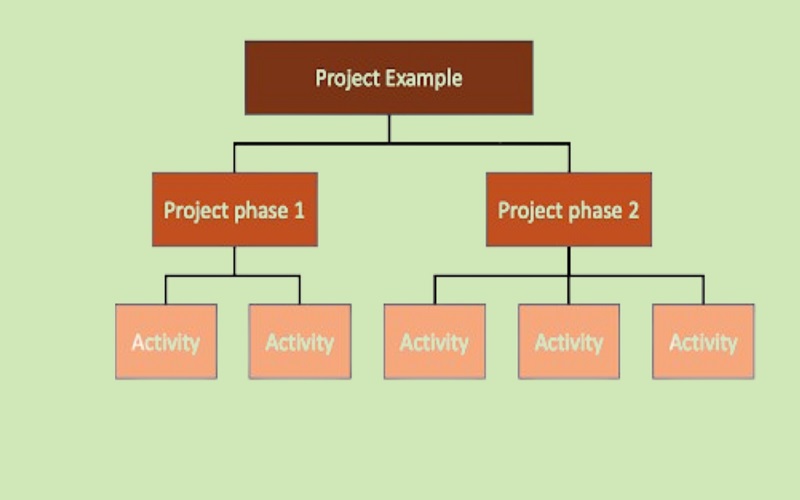
Agile estimation techniques follows a top-down approach. The project team makes gross-level estimation for different parts of the project. As the project progresses, detailed information is received at each particular stage.
In Agile estimation, tasks are divided based on story points. Story Points in Agile Project Management help identify and estimate difficulties in executing a specific user story. A lesser complex task will rank lower on the story point scale and an extremely complex task will rank high. There are four stages of Agile planning:
- The first stage involves pre-planning in which product backlog is considered, such as gathering vital information about the project, team formation, etc.
- The second stage involves planning in which any iterations or modifications are planned.
- The third stage involves release-planning in which the product team focuses on incremental releases and iterations.
In the last and fourth stage, the focus of project team is to complete high-priority Product Backlog modules.
Now, that we have understood the concept of Agile estimation, let us check the top 10 Agile estimation techniques.
Consider the following factors before selecting a technique:
- Team size
- The number of tasks to estimate
- Tools and resources available
- Working style of the team
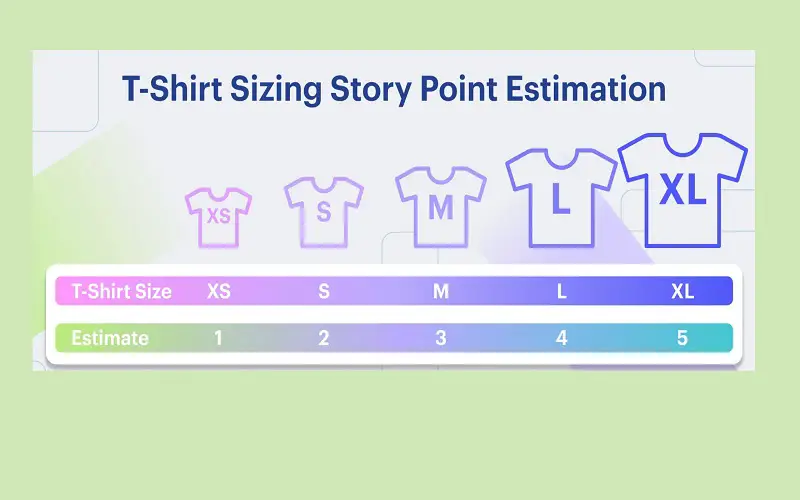
1. T-Shirt Sizing
Shirt sizing agile estimation technique is suitable for new project teams, large backlogs or early-stage estimations. It helps your team acquire a rough estimate of the task quickly. The technique is helpful for identifying significant user stories that require further breakdown. The product owner reads out the story in front of team members and asks them to estimate the time needed to complete the project. Estimations are made based on the t-shirt sizes, such as extra small(XS), small(S), medium(M), large(L), etc. T-shirt sizing technique helps in enhancing collaboration and creativity within the team.
2. Sprint Poker
Sprint Poker or Planning Poker is a collaborative Agile estimation technique based on a card system. The product owner reads the Agile story in front of the team. Once the story is complete, team members estimate the story points with the help of numbered cards. Then, these cards are placed on the table with face down. Each member picks one card and reveals the face of the card. By following these steps, the team members reach a consensus on final project estimation.
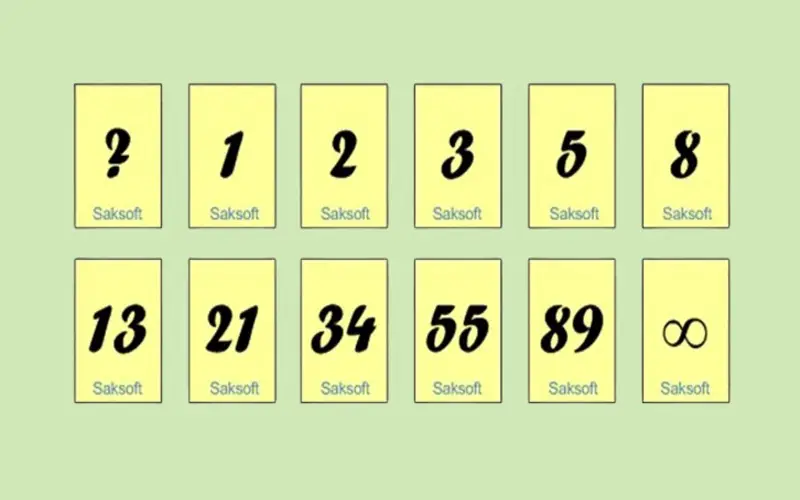
3. Affinity Mapping
Affinity mapping is an Agile estimation technique in which each team member selects one particular project or component and estimates its cost. In affinity mapping methodology, components are placed on the scale for their rankings, like a T-shirt scale or a Fibonacci scale. All the items are placed on the scale. Once the placement is complete, the team members mutually discuss the position of each item on the scale. They can also change the position of an item if needed and the process gets repeated until a final consensus is achieved.
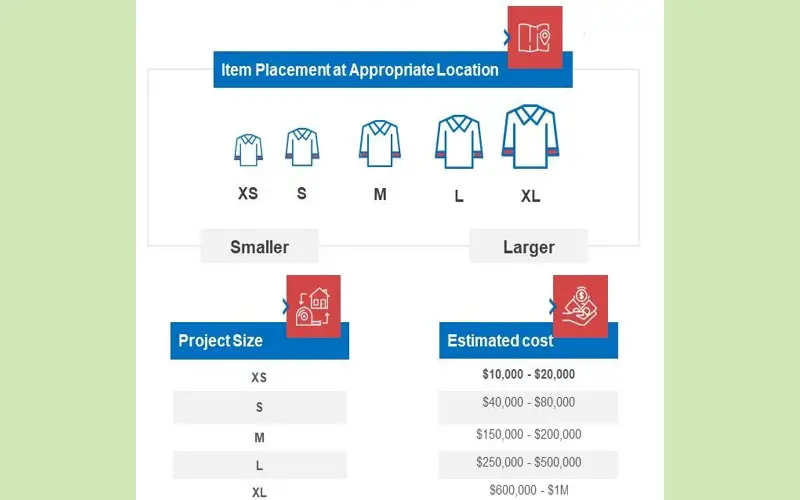
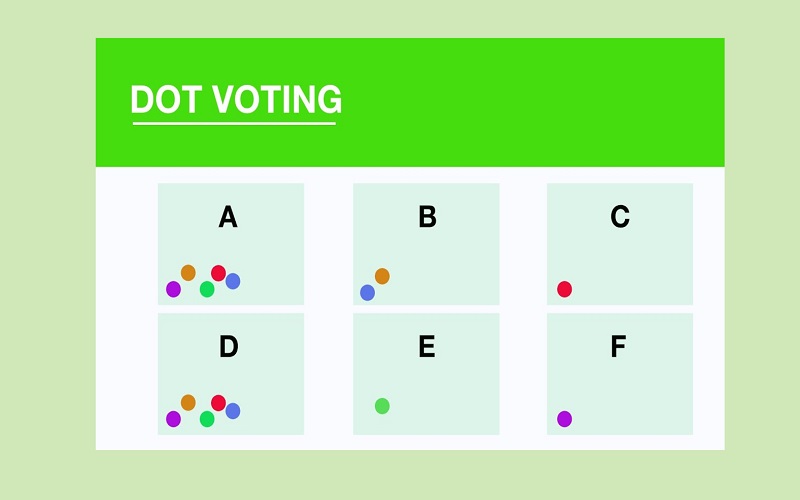
4. Dot Voting
The Dot Voting methodology is suitable for estimating small number sets. In this technique, participants use small dot stickers to vote on the size of project tasks. Each sticker represents one vote. The dot represents the time and resources needed to execute a project task. After several rounds of voting, one or more options are eliminated and all the team members agree mutually on the same time and resources needed for project completion.
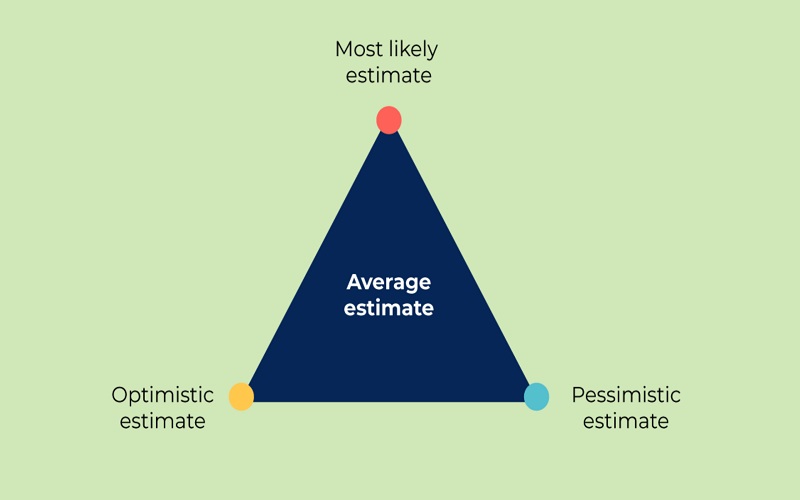
5. Three-Point Estimate
Three-Point Estimate is an Agile estimation technique based on Averages. There are basically three types of estimations involved in the technique: an optimistic estimation, a pessimistic, and the most likely estimation. The final estimation is made by calculating the basic average of all three estimations. The average is calculated by adding all three estimations and dividing the resultant figure by three. They can also perform weighted average as an alternative in which the most likely outcome is counted multiple times to achieve desired estimation result.
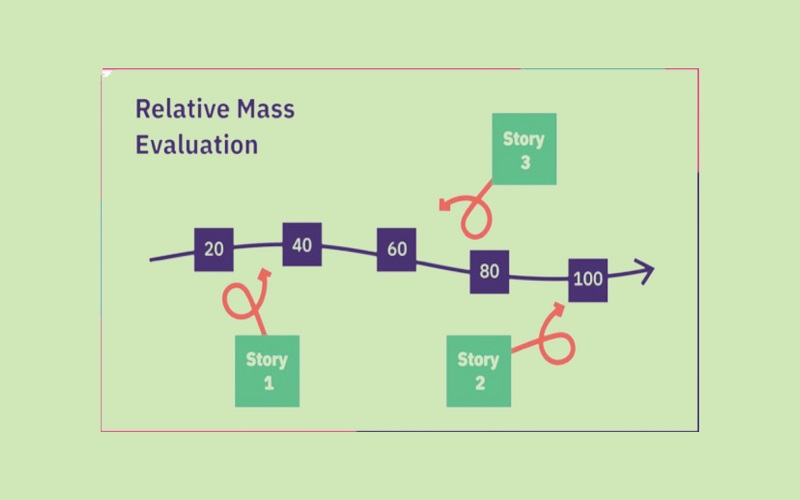
6. Relative Mass Evaluation
Relative Mass Evaluation technique is best for achieving precision and speed in Agile estimation. Also known as the Ordering Protocol, the technique considers utilizing all user stories and estimates their mass relatives to each other. The product owner reads the story and asks the team members to place their story on the scale based on their relative mass. Once all the stories are placed on the scale, team members can change the positions of stories to refine their estimates. The relative mass evaluation technique is most suitable in evaluating large number of items in short time frame.
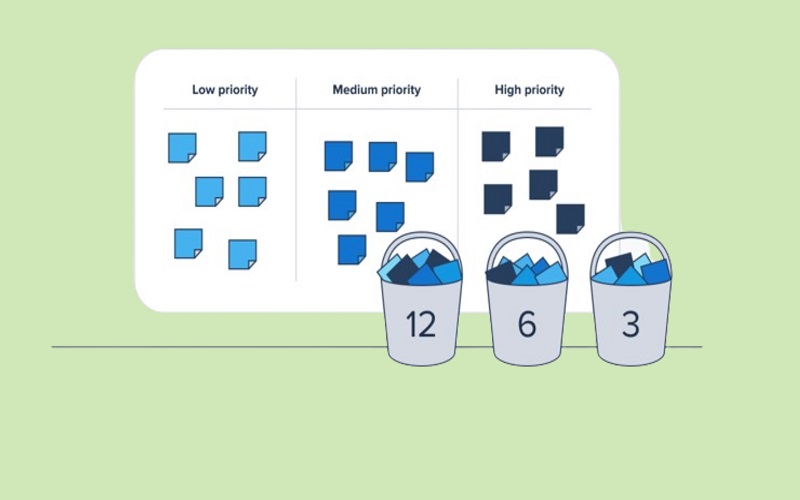
7. The Bucket System
In the Bucket system, user stories are placed in the buckets to make estimations. The team estimates individual stories and then puts them in the buckets. Each bucket has a number that represents the difficulty level in completing a project. The most challenging projects are placed in higher-numbered buckets, whereas more accessible projects are placed in lower-numbered buckets. After putting all the projects in the buckets, team members starts discussing each task and reach a final consensus.
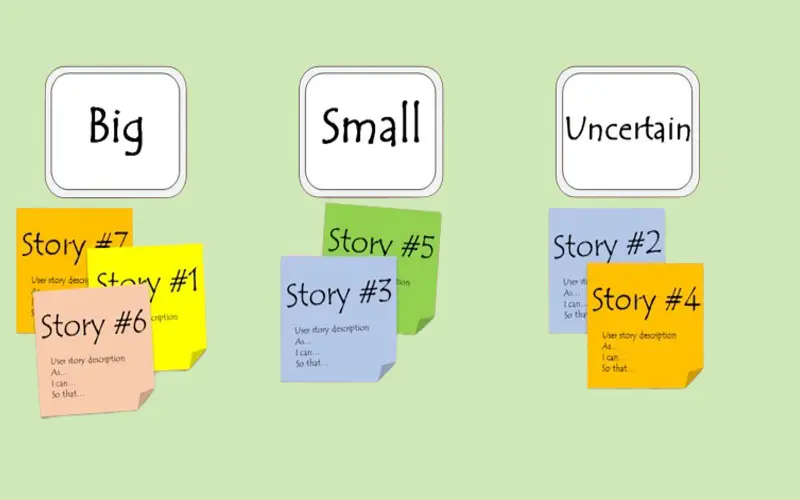
8. Big, Uncertain, Small
Big, Uncertain, Small technique helps make estimations for multiple projects or story elements. Each component classifies into three categories: big, uncertain, and small. The larger-size element is put under the big category and the small-size element is put under the small category. If the team has any disagreement regarding any aspect, then the element is put under the uncertain category. Team members mutually discuss user stories that are uncertain and re-evaluate them to identify areas where the stories lack context.
9. Story Counting
Story counting is an advanced estimation technique that estimates the average number of stories your team can complete within a given time. Story counting technique is based on the assumption that small and large items will balance out in long run, making it easy to plan and estimate the number of stories. To begin the process, user stories are combined into the appropriate effort ranges. After grouping, count the number of stories your team finished in the previous sprints. Based on prior figures, you can plan the number of user stories your team can achieve in the next sprint.
10. Top-down Estimate
In the Top-down estimate technique, the due date for task completion is informed by the facilitator. Participants divide themselves into groups and segment the project timelines into different phases. After allocating timelines for each project, the team members compare the estimates with each other. If any discrepancies are found, facilitators discuss it with the participants and ask them to make necessary changes.