Defragmentation of Active Directory Database
Active Directory:
There are many essential tools used in Microsoft Windows Servers and Active Directory is just one of the core tools present in Window Server platforms. It is important to define what Active Directory before explaining what Active Directory Database is.
Active Directory is a Microsoft technology that provides a variety of directory and network services. It was first released in Windows Server 2000 edition. It was later revised to improve administration and functionality in Windows Server 2003. Additional changes were made in Windows Server 2003 R2. Active Directory was later named as Active Directory Domain Services after further improvements and is one of the latest features of Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Active Directory Database:
Active Directory Database is one of the core tools of Active Directory that refers to the storage and management of directories. Active Directory database saves data into partitions so that the data can be segmented in an appropriate order and then retrieved efficiently when required. Microsoft refers to these partitions and data stores as ‘naming context’. Active Directory database is an important tool used to recover lost or corrupted data and to repair database in such cases. Extensible Storage Engine also known as ESE is an Active Directory Database used to manage all the objects of Active Directory in a Database. ESE uses different types of log files in order to manage and maintain the database.
Fragmentation and Defragmentation:
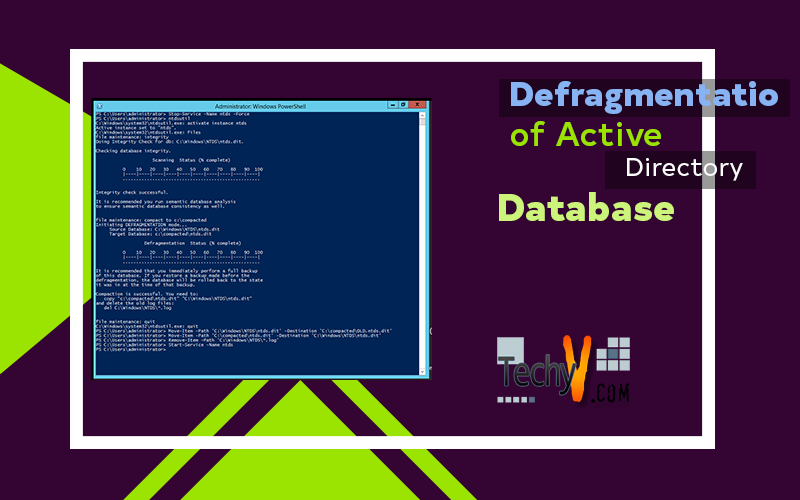
Fragmentation occurs as a result of deleting and adding new records in a database over a period of time which reduces the efficiency of Active Directory. Along with this, fragmentation also slows down the overall performance of Active Directory that affects the system performance of your computer. Defragmentation is performed to overcome such problems and keep the Active Directory in an efficient state. While updating records the data is stored in random sections where the defragmentation process updates this randomly saved data into contiguous sectors. This process increases the speed of access and retrieval of data and keeps the overall efficiency to the maximum.
Defragmentation is performed by moving a database to a new location and the original file is not deleted in this process. Hence, the original database can be used in case the defragmented file is not working. It also allows copying to a different hard drive in order to perform hardware maintenance. There are two types of defragmentation; online and offline. Online defragmentation is performed automatically every 12 hours by default as part of Garbage Collection Process and it does not reduce the size of database file. Moreover, online defragmentation optimizes data storage and reclaims space for new objects in the directory. Offline defragmentation, however, is manually performed by System Administrators and it reduces the size of database file and saves disk space. The offline defragmentation can only be performed while the database is inactive.
Comparison of Active Directory Database versions:
Active Directory Database and its defragmentation process are the same in Active Directory 2003 and Active Directory 2008. Hence, the process of offline defragmentation and online defragmentation is performed in the same manner for both 2003 and 2008 versions. However, there have been added new features in Active Directory 2008 and Active Directory 2008 R2 compared to Active Directory 2003 and Active Directory 2003 R2 in terms of objects and tools but the database process and defragmentation has remained the same.