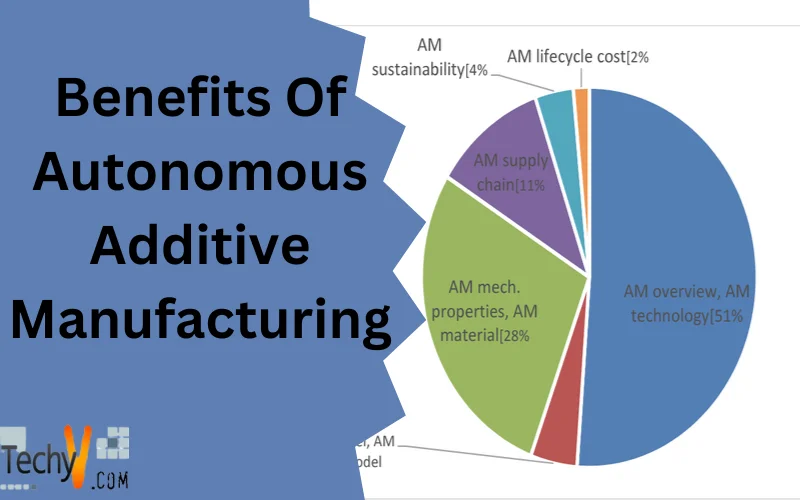
What Is Autonomous Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is growing respectable structures that are implementing this innovation to operate the design, extraction, and printing of required parts in real-time, with high quality. Additive manufacturing transforms both the procedures and product via the support of highly educated engineers working with manufacturers to digitally integrate, repair and stimulate components and processes in a revolutionary manner.
Best Practices For Autonomous Manufacturing
The two most significant products manufacturers can do to compose manufacturing systems to achieve the aim of autonomous manufacturing are: Recognize and save production data. As soon as a plant can start saving resultant data, it opens the opportunity to use that data to evaluate the future. That’s what manufacturers can do now if they haven’t yet started. Enhance the quality system. To improve quality, it’s significant to ensure that the information of the damage is noted (type, location, and discussion), and not just the reality that a detection has occurred.
1. Lower Start-up Costs
Manufacturing start-up costs can be prominent. The requirement to generate custom tooling for any latest item you wish to construct can control the scope of what is inexpensively attainable to produce. Industrial AM machinery costs as little as some thousand ponds, with home or devotee solutions close to a few hundred. When the time comes to convert your patterns, quickly tell the 3-D printer what the new pattern should look like. There’s no reason to throw away your investment in AM equipment.
2. Reduced Raw Material Wastage
Many standard forms of construction start with a larger block of metal or composed of wood and then minimize it. The fragments of materials that have been reduced are frequently of no economic use. These minimal manufacturing strategies waste a lot of raw materials. Additive manufacturing begins with nothing and then adds what is required, minimizing raw material wastage by up to 90 percent.
3. Personalization To The Individual
Because each 3D-printed item is based on a digital blueprint, it is simple to create each item rare without the requirement for retooling. This capability is a particular strength for the medical and healthcare section, where custom-made chips and supports can be customized to an individual. Research on using additive manufacturing methods to construct remaining human parts, such as bone, is also underway.
4. Digital Design Integration
Computer Aided Design (CAD) saw the transfer from the 2D drawing board to a world of 3D virtual design. Additive manufacturing takes this a step opposite and enables those virtual 3D patterns to be accomplished in the physical world at the touch of a button. Many design packages now support 3D printing ability, helping to automate required pattern steps, such as the involvement of inside penetrated strengthening or extrinsic platform. Additive manufacturing means it has never been simpler, quicker, or cheaper to render a 3D design into a physical object.
5. Less On-Hand Inventory
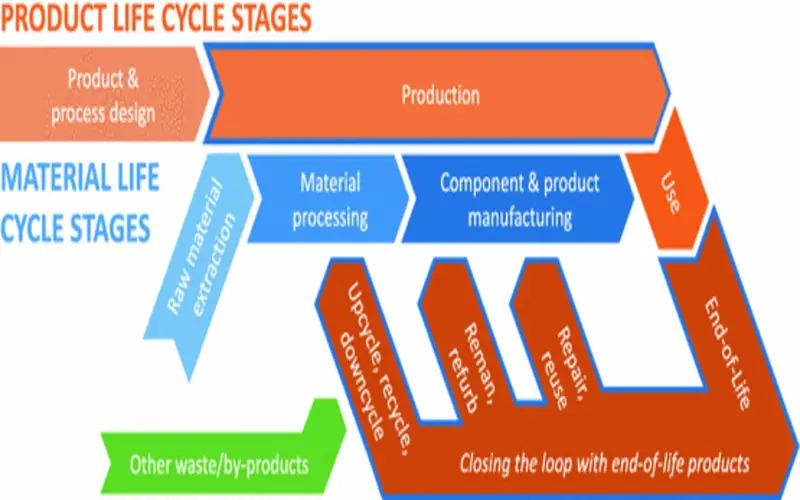
Standards manufacturing will stick you with a repository entire of premade components to draw from when you require removal. If you have to recollect or retire an old design, those impractical parts turn to scrap. Additive manufacturing enables you to have a virtual directory alternatively. You preserve the shared details in the cloud throughout the product life process and then print the required parts. That eliminates the need for repository space, personnel, and collection of obsolete parts.
6. Minimizes Energy And Environmental Costs
Additive manufacturing can benefit the environment by reducing manufacturing time and waste materials. Common Electric recently celebrated its 3D-printed gasoline beak tip for the LEAP engine. Under the additive manufacturing strategy, the number of parts in a particular fuel beak tip is minimized from 20 sections previously welded together to one whole section.
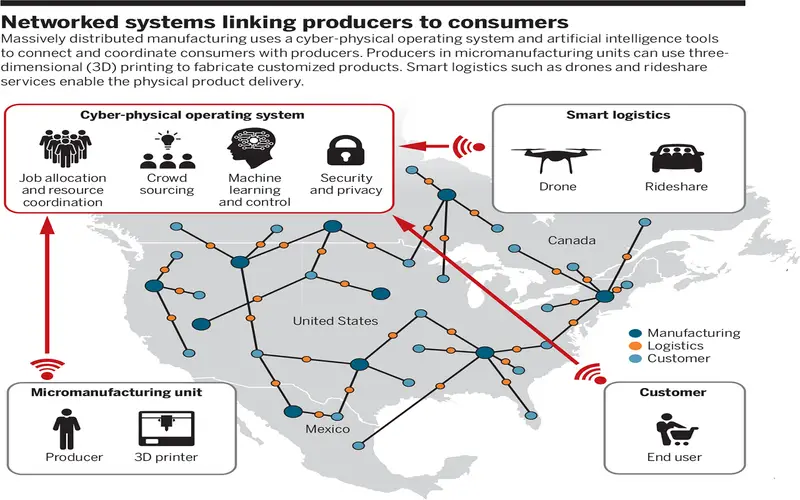
7. Distributed Manufacturing
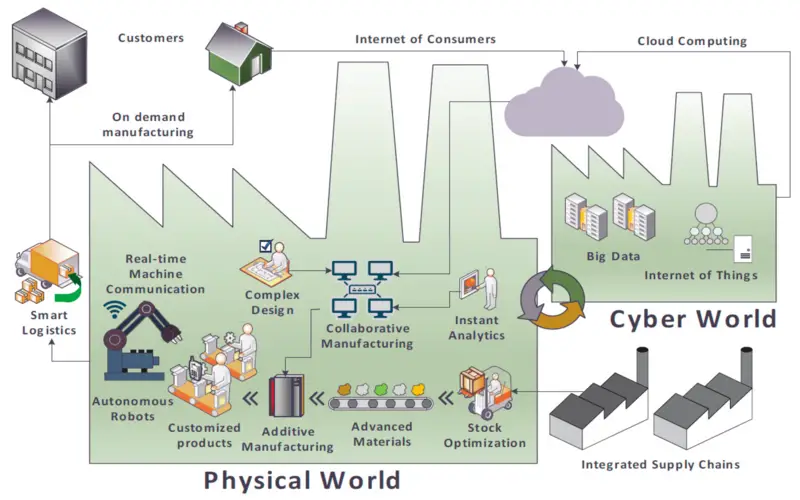
Another benefit of Additive Manufacturing is that creation is no longer required to be consolidated. Quickly place a 3D printer wherever you need the item to be produced this is one of many reasons that 3D printing will be used substantially distributed strategy might be complex. As an excessive example, NASA launched the “3D-Printed Habitat Challenge” a contest to build a 3D-printed habitat for deep space investigation, involving the agency’s travel to the moon, mars or beyond.
8. Allow An Accelerated Time-to-market
All firms confront challenges in terms of expediting new product introduction (NPI), being first to market, and responding quickly to customisation requests. Because additive manufacturing doesn’t need bulky tools or mold revisions, the time and costs of production change-over are eradicated. The essential benefit they expect to obtain from additive manufacturing is conveying faster. Around generating designs to be transported as components, additive manufacturing enables companies to print parts at point-of-need so they can be gathered into other products rapidly and effectively. There are no hauling or packaging costs when running manufacturers this way.
9. Cost Of Entry Continually To Fall
You might think that dropping into any new production strategy demands a significant direct capital investment, but with additive manufacturing, that is not automatically true. The cost of access for AM has continually been falling. Industrial-quality printers are accessible, and so are the general materials. Specialized strategy and materials cost more, but for most requirements, it’s simple to get into the game.
10. Save On Material Waste And Energy
The core definition of 3D printing is systemically adding material until a part is generated. It begins with laying down a base layer of material, then and adding successive layers until the part is finished. You may need to file off nettle or supports that catch up the part during printing, but the overall waste is minimized, mainly compared to the standard production strategy. Integrating parts for production can also generate significant savings on energy and materials costs.