
Is the TLS web security protocol really effective or has it been compromised? How does it change the security of our personal information? Can we still protect our personal information or is all hope lost to do so?
Web Secutity Protocol Of TLS: Is It Really Effective?

In recent research, we have found that the TLS web security protocol has been compromised. Thus, the passwords, card numbers, etc. that we enter online for shopping or any other reason is no longer encrypted using SSL version 2. 33% of the servers world-wide have been attacked by this. However, security can be provided by just disabling the SSLv2 on your browser.
Web Secutity Protocol Of TLS: Is It Really Effective?

TLS is the short term for Transport Layer Security. It is a protocol that offers data integrity and privacy among two communicating software or applications. It is the most widely deployed security protocol today and is used for web browsers and other programs that require secure transmission of data over a network like VoIP, VPN, instant messaging, and file transfers.
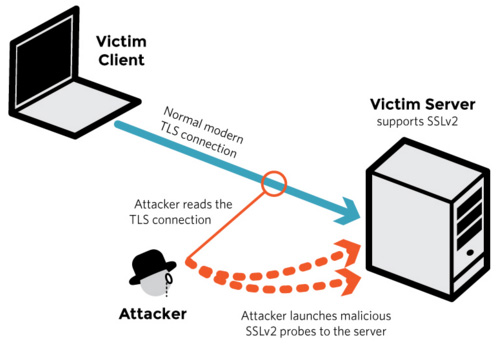
DROWN attack is one of the recently discovered form of attack that targets up-to-date TLS protocol suites. It is the short term for Decrypting RSA with Obsolete and Weakened eNcryption.
It is a kind of cross-protocol security bug attack that attacks servers that have the latest TLS protocol suites by utilizing their support for the outdated, vulnerable SSLv2 protocol to force an attack on connections that are using the latest protocols. In March 2016, the complete details about the DROWN attack were announced together with a patch that disables the SSLv2 protocol in OpenSSL.
This patch alone will not be enough to lessen the attack if the certificate is located on another SSLv2 host. Disabling the SSLv2 on all servers is the only practical countermeasure. As of March 1, 2016, it is estimated to about 33 percent (33%) of all HTTPS sites were affected by this vulnerability, according to researchers. The broken lock logo symbolizes the DROWN attack.

DROWN attack permits an attacker to decrypt HTTPS connections by transmitting specially crafted malicious packets to a server or if the certificate is shared on another server, potentially executing a successful MitM attack or Man-in-the-Middle attack.














