Asked By
L Smith
10 points
N/A
Posted on - 10/13/2016

Switching operates at layer 2 of OSI model whereas the Routing operators at layer 3. The devices in the same layer 2 do not require routing to local ones. Differentiate between layer 2 and layer 3 switches?
Answered By
d.anupom
10 points
N/A
#93057
2 Layer To Send The Traffic And Route It To The Host.

PC A wishes to transfer traffic to B. if A does not know the unique MAC address, it has to wait till it is discovered by ARP.
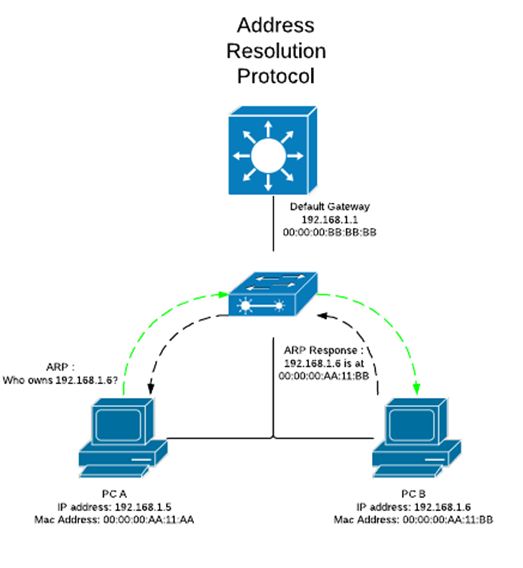
The packet will then be sent to the MAC address. Switch will further forward it to the port depending on the MAC address table.

There is a broadcast domain in the layer 2 switch.
The broadcast traffic is sent from the switch to all the ports leaving the one where packet arrived. These do not pass from layer 3. Large domains can have problems like broadcast storms.

t is preferred to keep some clients into different domains for the security. It is done as the time of configuration of VLAN’s. VLAN’s provide flexibility. They allow different layer 3 networks to share the single layer 2 structure. VLAN’s have their own layer 3 structure. Layer 3 switches perform switching as well as routing operations. PC sends the traffic. Layer 2 accepts the packet. It will be routes to the destination depending on the route table.
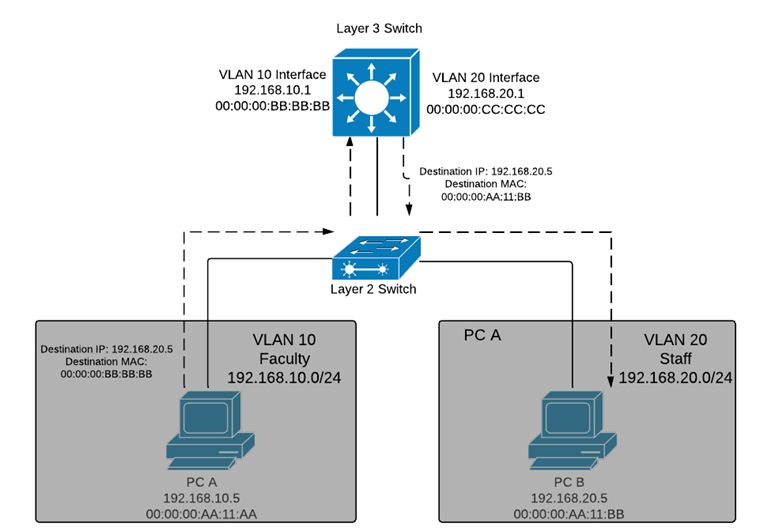
The above figure shows an traffic transfer between 2 VLAN’s.












